Cybercriminals continue to efficiently populate their botnets, through the systematic and persistent spamvertising of tens of thousands of fake emails, for the purpose of socially engineering gullible end users into executing the malicious attachments found in the rogue emails.
We’ve recently intercepted a currently circulating malicious campaign, impersonating Barkeley Futures Limited, tricking users into thinking that they’ve received a legitimate “Customer Daily Statement”.
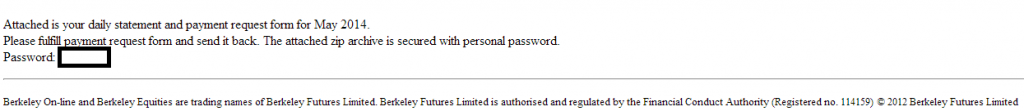
More details:
Sample screenshot of the spamvertised email:
Detection rate for a sampled malware: MD5: b05ae71f23148009c36c6ce0ed9b82a7 – detected by 29 out of 54 antivirus scanners as Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Foreign.kxka
Once executed, the sample starts listening on ports 16576.
It then creates the followung Mutexes on the affected hosts:
Local\{6FC54A61-D264-7CF8-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Local\{21D28140-1945-32EF-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Local\{3C2F38F1-A0F4-2F12-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{29B0195A-815F-3A8D-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{1D55DC30-4435-0E68-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-1BA9-177341D093D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-1FA9-177345D093D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-7BA8-177321D193D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-43AB-177319D293D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-6BAB-177331D293D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-87AB-1773DDD293D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-B3AB-1773E9D293D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-5FAA-177305D393D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-8FAA-1773D5D393D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-F3AA-1773A9D393D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-03AD-177359D493D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-53AD-177309D493D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-9BAC-1773C1D593D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-FFAC-1773A5D593D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-87A9-1773DDD093D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-F7AD-1773ADD493D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-EBAD-1773B1D493D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-03AC-177359D593D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-07AF-17735DD693D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-5FAD-177305D493D1}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-3BAE-177361D793D1}
Global\{5E86DCC0-44C5-4DBB-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{68DA68FA-F0FF-7BE7-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{24816566-FD63-37BC-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{32526B1B-F31E-216F-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{7BF19192-0997-68CC-43AF-177319D693D1}
Global\{4E6EC1F5-59F0-5D53-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Once executed, the sample drops the following malicious MD5 on the affected hosts: MD5: ed54fca0b17b768b6a2086a50ac4cc90
It then phones back to the following C&C servers:
62.76.43.110
62.76.185.94
Related malicious MD5s known to have phoned back to the following C&C server (62.76.43.110):
MD5: c02e137963bea07656ab0786e7cc54de
Once executed, the dropped MD5: ed54fca0b17b768b6a2086a50ac4cc90 starts listening on ports 35073.
It then creates the following Mutexes on the affected hosts:
Local\{6FC54A61-D264-7CF8-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Local\{21D28140-1945-32EF-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Local\{3C2F38F1-A0F4-2F12-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{29B0195A-815F-3A8D-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{1D55DC30-4435-0E68-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-1BA9-177341D093D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-1FA9-177345D093D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-7BA8-177321D193D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-43AB-177319D293D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-6BAB-177331D293D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-87AB-1773DDD293D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-B3AB-1773E9D293D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-5FAA-177305D393D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-8FAA-1773D5D393D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-F7AA-1773ADD393D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-3BAD-177361D493D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-5FAD-177305D493D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-9FAC-1773C5D593D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-F3AC-1773A9D593D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-D3A9-177389D093D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-FFAD-1773A5D493D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-03AC-177359D593D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-1BAC-177341D593D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-23AF-177379D693D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-6FAE-177335D793D1}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-E7AD-1773BDD493D1}
Global\{5E86DCC0-44C5-4DBB-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{32526B1B-F31E-216F-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{68DA68FA-F0FF-7BE7-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{24816566-FD63-37BC-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
Global\{99B500D9-98DC-8A88-0BAD-177351D493D1}
Global\{4E6EC1F5-59F0-5D53-D58B-19468FF29DE4}
It also phones back to the following C&C servers:
62.76.185.94
23.62.99.40
Related malicious MD5s known to have phoned back to the following C&C server (23.62.99.40):
MD5: 94779039810a15eb828ff0a14de284a3
MD5: 45035e1785e71db9a9abc2510493deec
MD5: 6cf791e6a6e68b365eefb1b379937539
MD5: b7ad50bc3b09cc1883b6fb01fca2b1a5
MD5: a724dfc02ae9c1b9f6ef6b3cb6cd3b6a
MD5: b2fe7e4dcd216bf66609630b85d70e80
MD5: bd0f89628a591cf788c836a00a5e3125
MD5: b2859c8bb58806999d7d2603d200d2da
We’ll continue monitoring the campaign, and post updates as soon as new developments take place.
Webroot SecureAnywhere users are proactively protected from these threats.