
by Blog Staff | Mar 9, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
On a daily basis, spammers register thousands of new domains across multiple domain registrars, and take advantage of WHOIS privacy services to ensure that security researchers and anti-spam fighters will have hard time taking them down. So what can we do about it?
According to a newly released research by Knujon.com, proper screening could have prevented 67% of those abusive domain registrations.
More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Mar 8, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
With politically motivated DDoS (distributed denial of service attack) attacks proliferating along with the overall increase in the supply of managed “DDoS for hire” services, it’s time to get back the basics, and find out just what makes an average DDoS bot used by cybercriminals successful.

Continuing the “A peek inside…” series, in this post I’ll profile the Darkness X (Optima) DDoS bot, available for purchase at selected cybercrime-friendly online communities since 2009.
More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Mar 8, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
Cybercriminals are currently spamvertising a fraudulent email campaign impersonating Citi, using ‘Temporary Limit Access To Your Account‘ themed emails as a social engineering attempt to trick end users into clicking on the link found in the phishing emails.
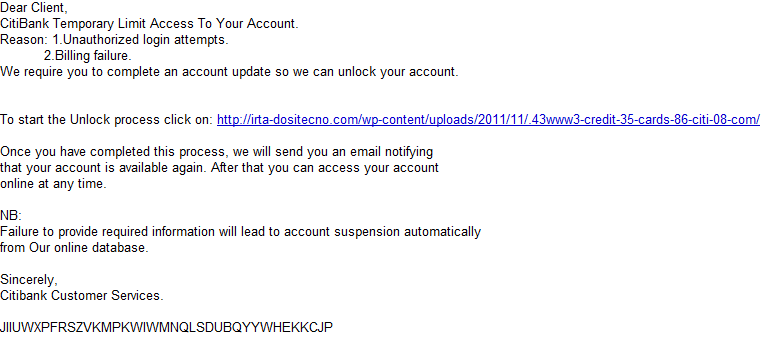
More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Mar 6, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
by Nathan Collier
Android.SMS.FakeInst is a Trojan that aims to do one thing — trick users into sending premium SMS messages by pretending to be an install for an app. Here’s how the scam works: The user sends three premium SMS messages in exchange for an app, but there is no guarantee that it will actually install anything after they already have your money. These malicious apps are getting harder and harder to discern as malicious as the look and feel of these apps get better through newer iterations. One variant of these Trojan apps, which comes from a known malicious site, looks better with each update. Let’s start with one of the first iterations of this variant.
The icon looks fairly convincing:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Mar 2, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
What happens when a host gets infected with malware? On the majority of occasions, cybercriminals will use it as a launch platform for numerous malicious activities, such as spamming, launching DDoS attacks, harvesting for fresh emails, and account logins. But most interestingly, thanks to the support offered in multiple malware loaders, they will convert the malware-infected hosts into anonymization proxies used by cybercriminals to cover their Web activities.
In this post, I’ll profile a newly launched service, offering thousands of malware-infected hosts as Socks4 and Socks5 servers for anonymizing a cybercriminal’s Web activities.
(more…)










