It can be easily argued, that CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart), is the modern day’s ‘guardian of the Web’, in the context of preventing the mass, systematic, and efficient abuse of virtually each and every Web property there is.
Over the years, CAPTCHA developers continued to strike a balance between the actual usability and sophistication/resilience to attacks, while excluding the beneath the radar emergence of a trend, which would later on prove to successfully exploit a fundamental flaw in the very concept of the CAPTCHA process. Namely, the fact that, the very same humans it was meant to differentiate against the automated bots, would start to efficiently monetize the solving process, relying on the ‘human factor’, instead of applying scientific based type of attack methods.
Acquired by Google in 2009, reCAPTCHA, quickly emerged as a market leader in the space, leading to good old fashioned (eventual) exploitation of monocultural type of flaws, applied not just by security researchers, but naturally, by cybercriminals as well. How do cybercriminals bypass the Web’s most popular CAPTCHA? Do they rely on human-factor type of attacks, or continue aiming to scientifically break it, like it is most commonly assumed by CAPTCHA developers? Based on the average response times that we’re aware of, a newly launched CAPTCHA-solving/breaking service, that’s exclusively targeting Google reCAPTCHA, might have actually found a way to automate the process, as we’re firm believers in the fact that, no ‘CAPTCHA solving junkie’, can solve a reCAPTCHA in less than a second. Let’s take a peek inside the service, discuss its relevance in the CAPTCHA-solving/breaking market segment, and why its reliance on an affiliate network type of revenue sharing scheme, is poised to help the service, further acquire high-end customers, namely vendors of blackhat SEO/spam tools.
Despite the numerous and persistent attempts we’ve observed over the years, on behalf of efficiency-oriented cybercriminals, relying on machine-learning CAPTCHA breaking attack scenarios, further fueling growth of the ever-green underground market segment for automatically registered bogus accounting data, in 2014, based on our situational awareness, low-waged human CAPTCHA-solvers, remain the primary attack tactic of choice. A fact which naturally leads to a vibrant fraudulent ecosystem, whose existence continues empowering market leading blackhat SEO (search engine optimization) and spamming tools, with real-time CAPTCHA-solving capabilities, consequently account registration/Web property abuse capabilities. Largely relying on an API-based type of platforms, as well as the non-stop supply of clean IPs through the use of compromised hosts as proxies, the CAPTCHA-solving market segment continues getting populated by new entrants, the bulk of whose CAPTCHA-solving activities, gets outsourced to 24/7/365 operating CAPTCHA-solving farms, like the ones I extensively researched back in 2007, and 2008.
What’s new in 2014? As we’ve been monitoring a newly launched CAPTCHA solving/breaking service for a few days now, it’s time to take a peek inside its customer’s interface, to showcase its unique differentiation factors.
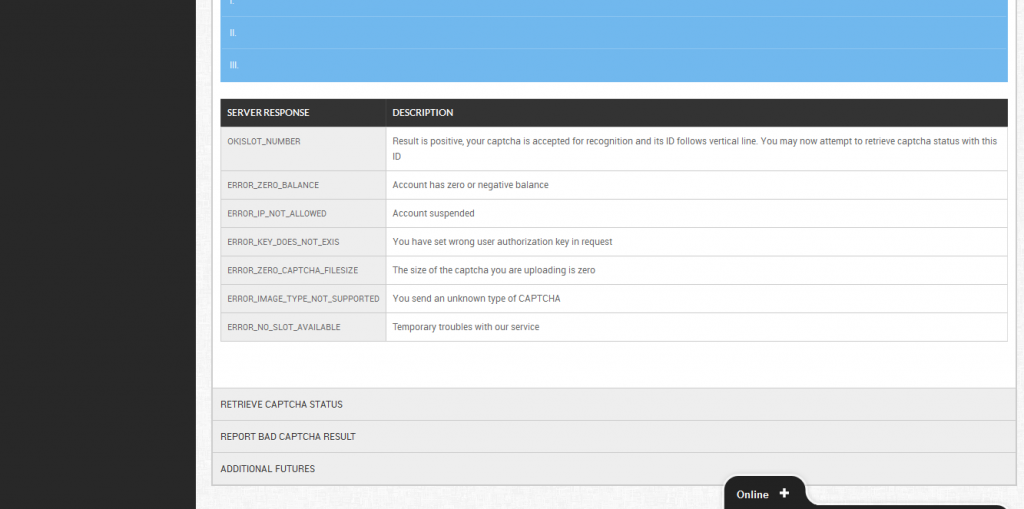
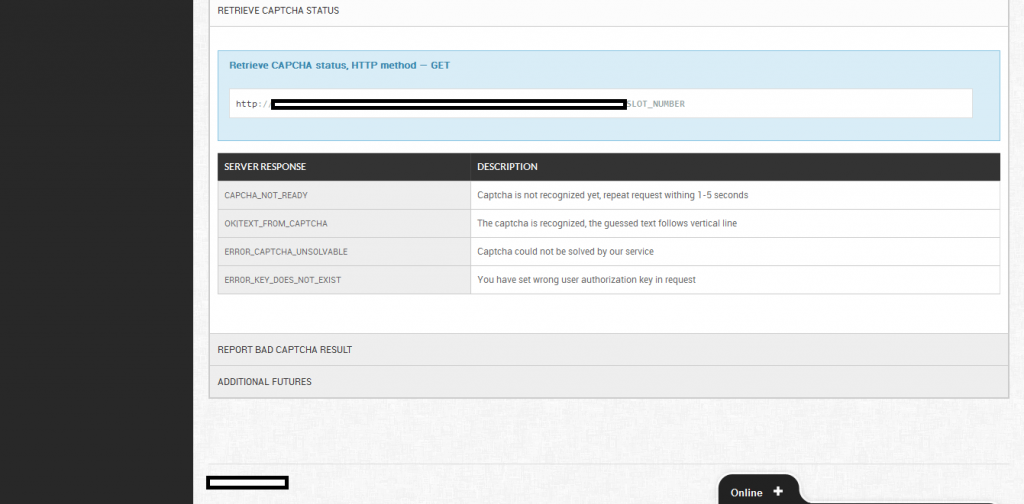
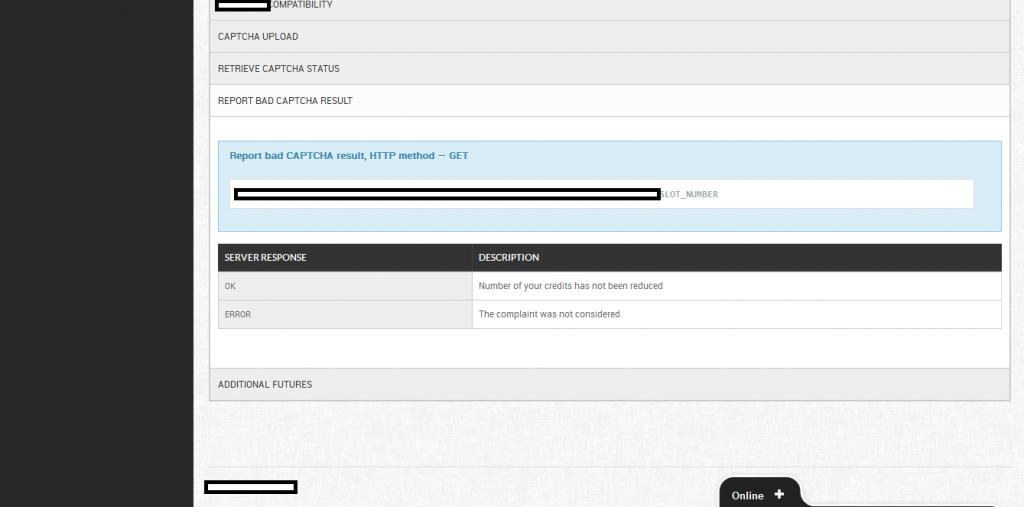
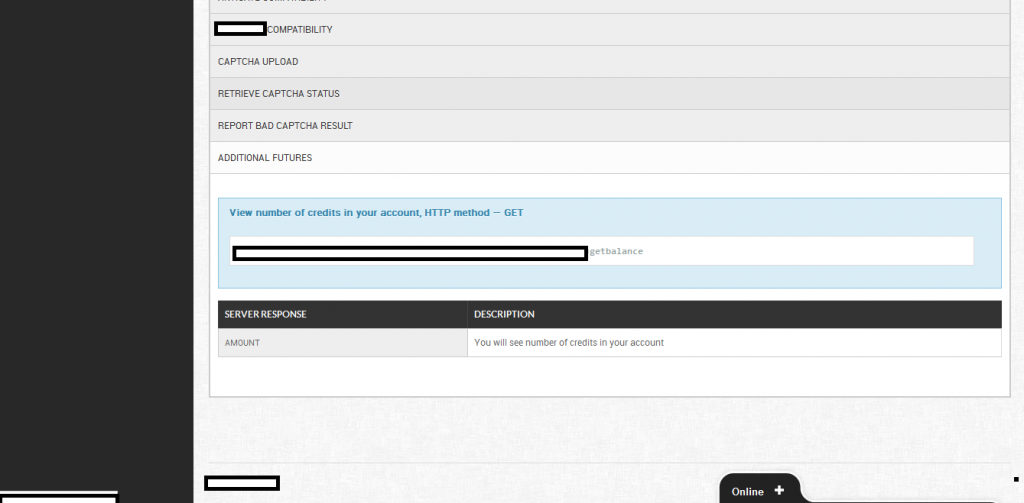
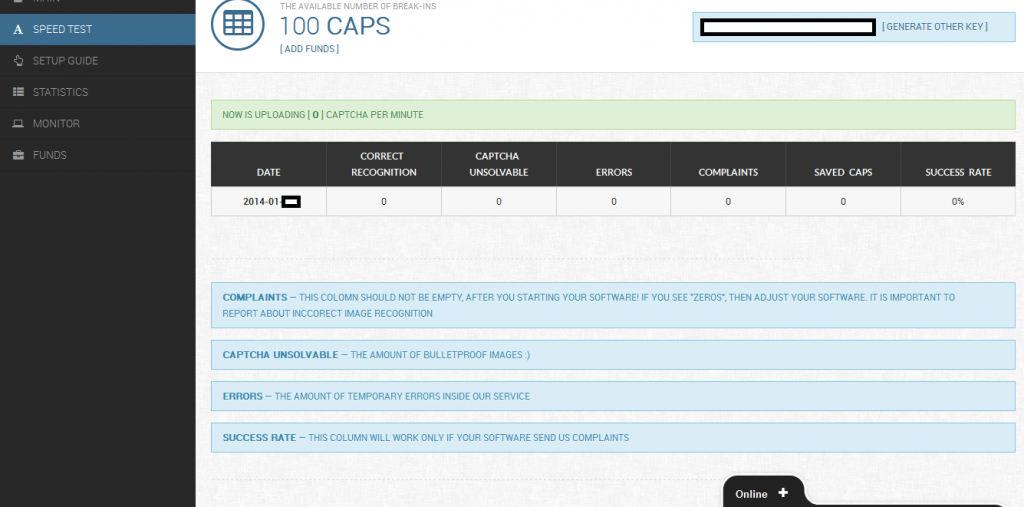
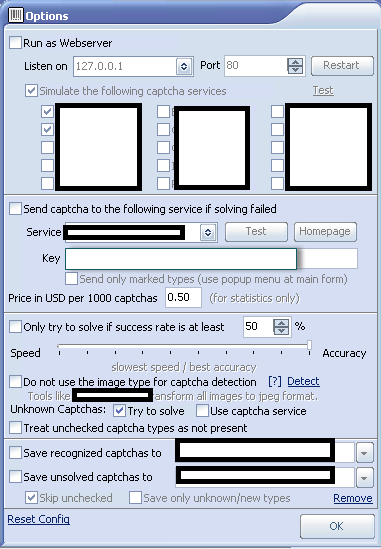
Sample screenshots from within the customer’s interface of the reCAPTCHA solving/breaking service:
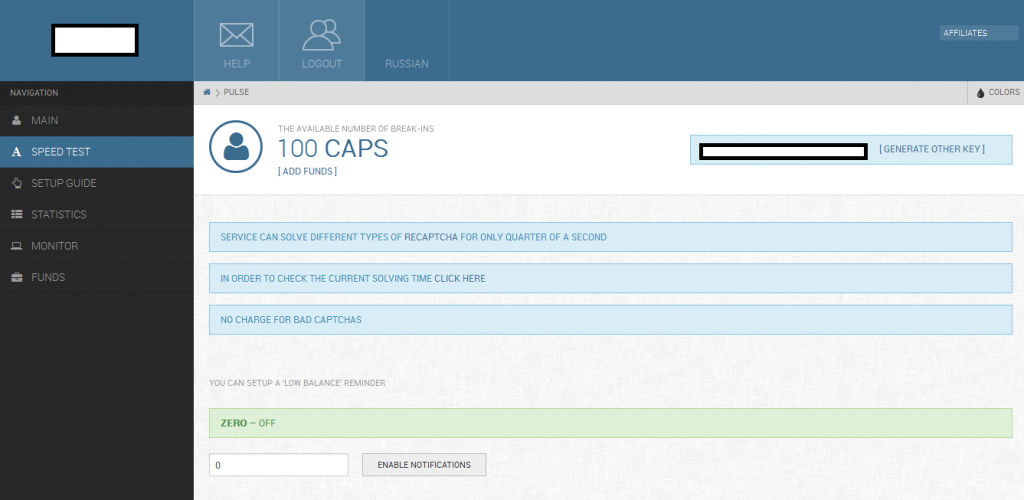
Average time for solving a reCAPTCHA using the service:
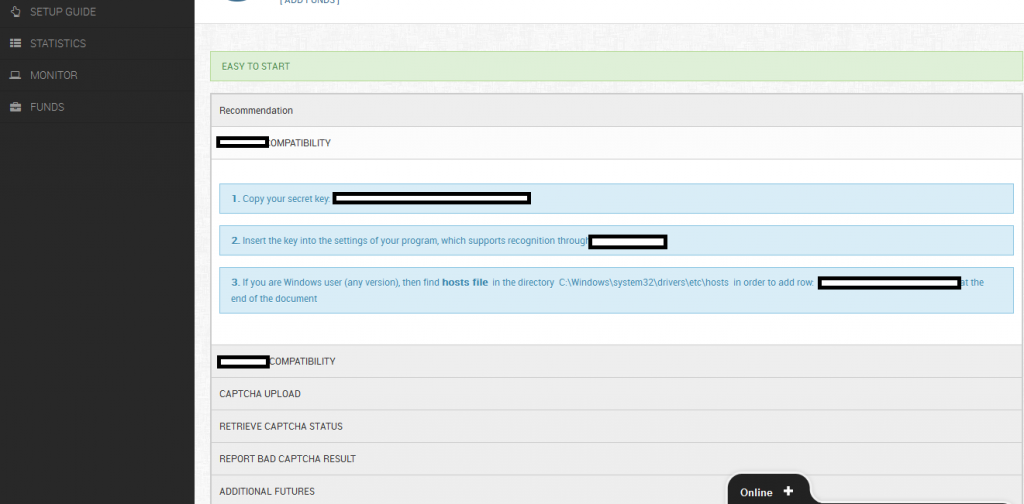
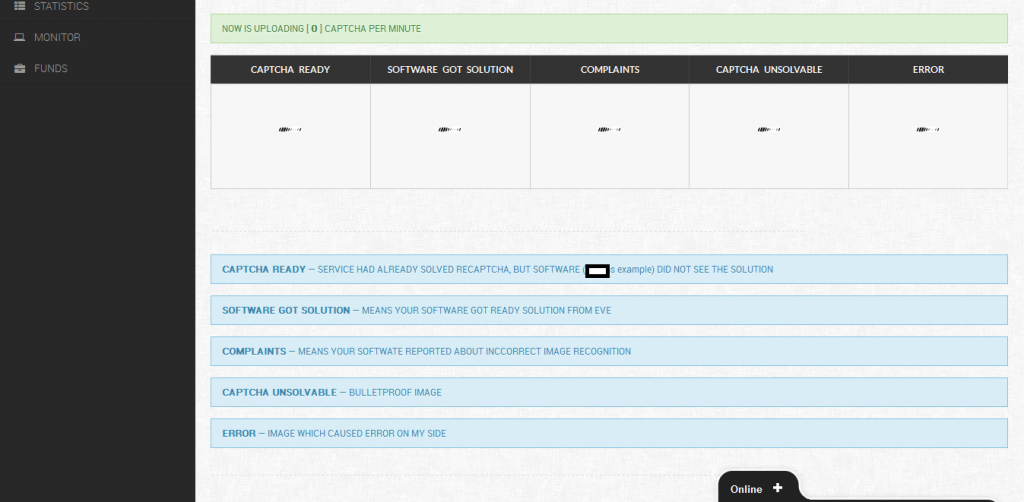
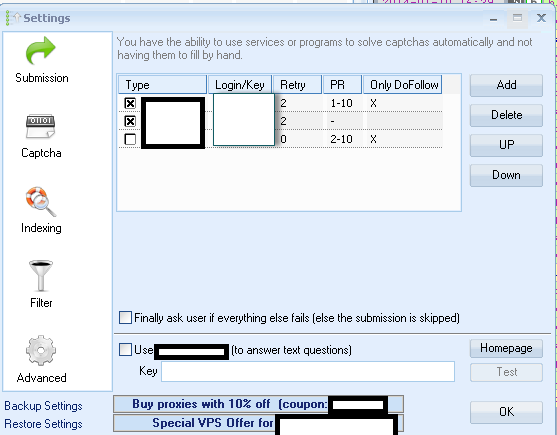
Related screenshots from within the customer’s panel, demonstration the degree of automation offered to customers:
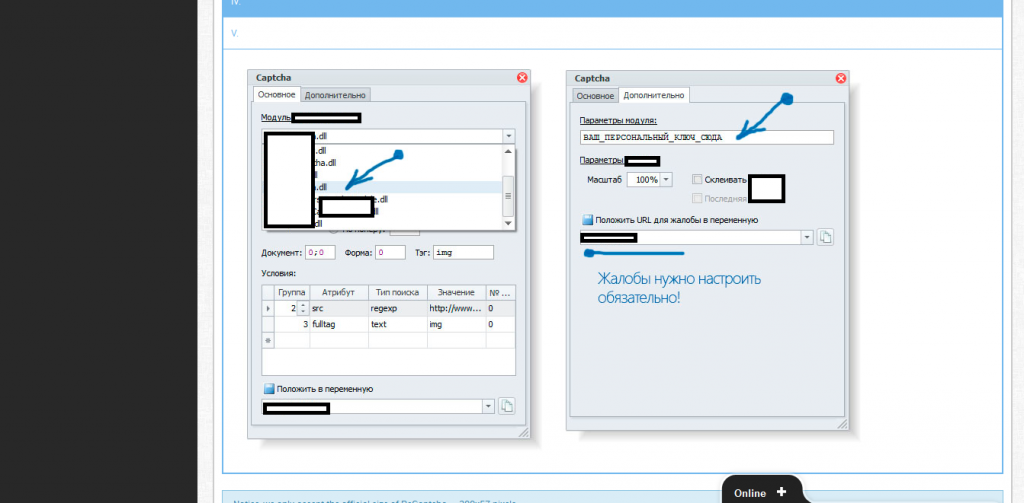
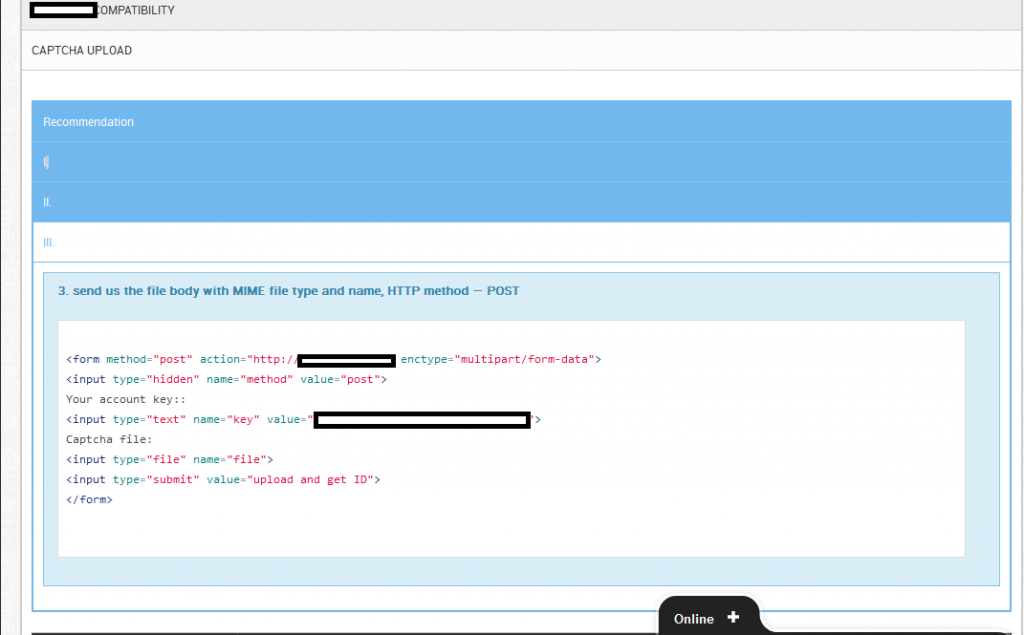
Sample screenshots confirming the ongoing integration of the managed reCAPTCHA solving/breaking service, within popular blackhat SEO/spamming tools:
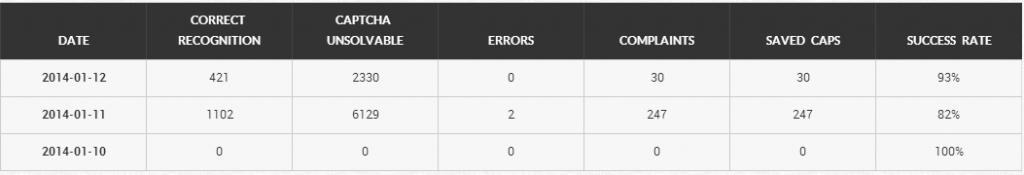
Sample percentage statistics for solved/unsolved reCAPTCHAs using the service in action:
We believe that the service is relying on a machine-learning approach — based on the statistics obtained for the average time required to solve/break a reCAPTCHA which in this case is less than second — primarily syndicating clean IPs, through managed services offering an endless supply of malware-infected hosts (Socks4/Socks5), in an attempt to adapt to reCAPTCHAs challenge-response machine learning detection process, which works in a fairly simple way. The higher the probability/indication that a request is made in an automated fashion/bad IP reputation, the harder the CAPTCHA challenge presented to the human/bot. Therefore, we believe, that, it is the overall availability of malware-infected hosts within the underground marketplace, that’s acting as a crucial success factor for the service’s success, which, of course, should not exclude the machine learning approach which we believe is taking place as well.
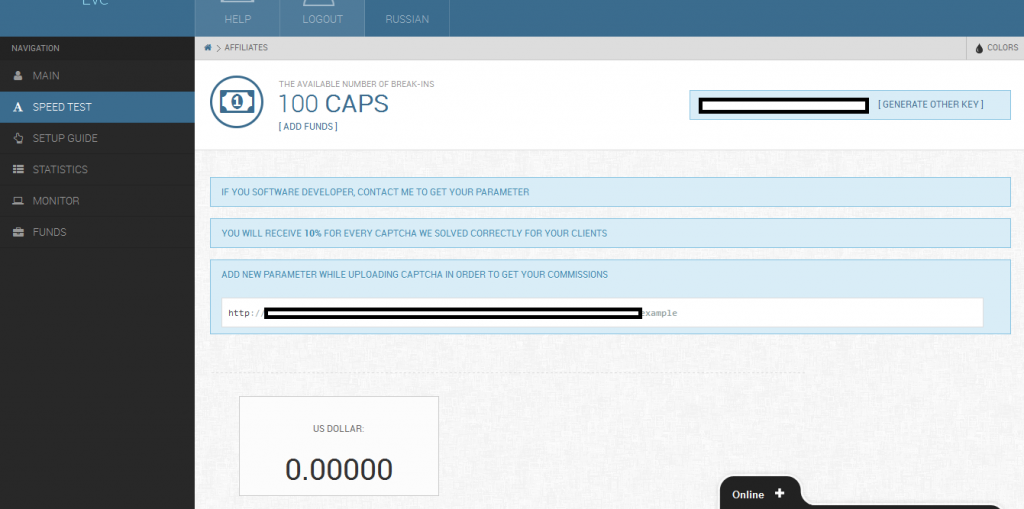
The key to success embraced by this new CAPTCHA solving/breaking market segment entrant? Not surprisingly, the ubiquitous for the cybercrime ecosystem in terms of proven growth factors, affiliate network based type of revenue sharing schemes. In this particular case, vendors of blackhat SEO/spamming tools are asked to contact the service, in order to get their unique perimeters, with the service offering them 10% for every CAPTCHA solved correctly on behalf of their customers. As always, the logical degree of profitability of the service, will be proportional with its ability to remain online, which sadly, wouldn’t be a problem in an extremely vibrant underground market segment offering bulletproof hosting services.
We’ll continue monitoring the development of the service, and post updates as soon as new developments emerge.







i like this recaptcha solver) the URL is http://www.eve.cm