‘Koobfox’ variant digs for Firefox cookies
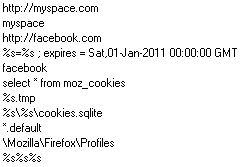 A new variant of the Koobface worm started striking out this week, with a twist: Where the older Koobface would steal and use the cookies saved by Internet Explorer which store social network logins in order to spread its infectious messages in the victim’s name, this new variant is pulling down a tool designed to steal credentials saved by Firefox (in the form of cookies and stored passwords). Users of the Firefox browser were, until now, able to thwart the pernicious spy’s ability to hijack a victim’s social network accounts, because the two browsers store their cookies in different locations, and in different formats.
A new variant of the Koobface worm started striking out this week, with a twist: Where the older Koobface would steal and use the cookies saved by Internet Explorer which store social network logins in order to spread its infectious messages in the victim’s name, this new variant is pulling down a tool designed to steal credentials saved by Firefox (in the form of cookies and stored passwords). Users of the Firefox browser were, until now, able to thwart the pernicious spy’s ability to hijack a victim’s social network accounts, because the two browsers store their cookies in different locations, and in different formats.
We got wind of the new variant as we saw the characteristic links spreading through various networks yesterday. In our early tests, the worm exhibited similiar skill at spreading over multiple networks: In addition to Facebook, the MySpace, Hi5, Friendster, Tagged and Netlog accounts we use for testing its behavior were used to spread malicious links, posted either to the victim’s “wall” or status, or as messages sent to all of the account-holder’s friends.
Using a well-documented hack to access the Firefox cookie file, the payload (appropriately named ff2ie.exe) looks for a copy of the file sqlite3.dll on the victim’s hard drive, then uses the functionality of that file to pull social network cookie information from the Firefox cookie database (as shown in the screenshot, above), and write an Internet Explorer cookie containing all that information. With the IE cookie(s) in place, the rest of the Koobface payloads work as they did before.
The worm continues to query the download server for payloads targeting 10 social networking services, but for an undetermined reason, it only delivered six targeted payloads. We also saw that, instead of downloading the executable payloads directly, the worm downloaded installers, each of which place various payloads in the Windows folder, then self-delete.
The WoW Catphishers are Biting

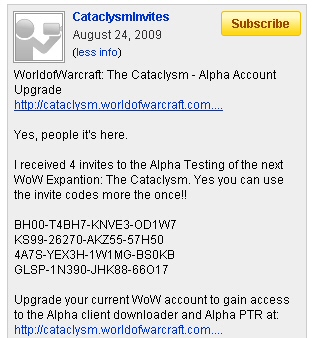 The body’s barely cold from last week’s BlizzCon, but the script kiddies who write phishing kits have been hard at work putting their best foot forward, crafting account-stealing code that targets gullible WoW players who want an early peek at the just-announced Cataclysm expansion. These Catphish pages, linked off of YouTube video postings that offer promises of early, exclusive access to the expansion, lift graphics and design characteristics directly from the pages hosted by Blizzard, the publisher of the WoW franchise.
The body’s barely cold from last week’s BlizzCon, but the script kiddies who write phishing kits have been hard at work putting their best foot forward, crafting account-stealing code that targets gullible WoW players who want an early peek at the just-announced Cataclysm expansion. These Catphish pages, linked off of YouTube video postings that offer promises of early, exclusive access to the expansion, lift graphics and design characteristics directly from the pages hosted by Blizzard, the publisher of the WoW franchise.
Unfortunately for the script kiddies making and hosting the pages, they’re making some of the most boneheaded mistakes imaginable.
Take, for example, this page. The creator of this page was so eager to get his l33t phishing site posted on his favorite message board, he forgot to take a close look at what he was including with his phish kit. It includes not only log files containing links to the live site where he’s hosting this phishing scam, but also to a site where he’s hosting another phishing scam intended to steal a promotional code given to WoW fanatics as a bonus after they paid to watch BlizzCon streamed live to their computer.
How Phishers Target WoW Players
 Yesterday, at the opening of our BlizzCon coverage, we showed you just how commonly phishers target WoW players by posting innocuous-looking links in message board or forums frequented by players. Today, we’ve produced a really short video that shows exactly how someone infects their computer with a phishing Trojan.
Yesterday, at the opening of our BlizzCon coverage, we showed you just how commonly phishers target WoW players by posting innocuous-looking links in message board or forums frequented by players. Today, we’ve produced a really short video that shows exactly how someone infects their computer with a phishing Trojan.
As you can see in the video (even through the “censorship”), the page the victim eventually ends up on emulates the appearance of a Flash-video-based porn site. Every single link on the page links to the malware installer, which means that no matter where on the page the victim clicks, he or she is presented with a download dialog box. Check it out.
[vimeo 6213917]
This simple social engineering trick, so commonly used of late by Koobface to fool social network users, still manages to convince people to execute the malware installer in order to view the video.
We’d all like to take a moment to give one simple piece of advice: If you follow a link and end up on a site you clearly weren’t intending to go to, stop. Don’t download any executable files—and absolutely don’t run any executable files if you happen to download them. If you have to, hit the Alt-F4 keyboard combination to kill the browser right there, but just don’t run anything else.
Misled gamers who download and run the flash “installer” won’t see any obvious difference on their computers to indicate that they are infected. At this point, the Trojan is ready to start stealing login credentials. These infections are often fairly simple in their configuration, though as with all malware there are much more complex versions that can steal the passwords for multiple games.
The installer executable simply drops a DLL file onto the victim’s hard drive, typically to the System32 or another Windows subdirectory. That file performs the keystroke logging, then sends that data to the phisher behind the scam. The installer also modifies the Registry so the DLL loads with every startup.
Keyloggers aren’t the only threats targeting online games. Others include spam phishing-type posts on the public forums for individual guilds, malicious URLs communicated through the in-game chat channels, and even exploits against security weaknesses in Web sites and message boards frequented by members of the WoW playing community.
BlizzCon, Gamers, WoW Trojans, Oh My
 Tomorrow morning, Blizzard Entertainment (the publisher of the wildly popular World of Warcraft franchise) will kick off another BlizzCon to show off their latest projects and directly interact with their fanbase. World of Warcraft will likely take center stage at the convention, which has become the venue of choice for Blizzard to unveil their newest expansion pack for the enormously popular online role-playing game.
Tomorrow morning, Blizzard Entertainment (the publisher of the wildly popular World of Warcraft franchise) will kick off another BlizzCon to show off their latest projects and directly interact with their fanbase. World of Warcraft will likely take center stage at the convention, which has become the venue of choice for Blizzard to unveil their newest expansion pack for the enormously popular online role-playing game.
Here at Webroot we have our fair share of past and present WoW players. So we’re quite tuned in to the malware that plagues WoW and other online games. As the gaming market continues to grow at an amazing rate, so does the real-money value of (and the virtual currency stored in) game accounts used in association with those games.
Earlier this summer we shared with our readers the top ways that threats get introduced into online games and the best ways to avoid them. With Blizzcon just hours away, and the WoW servers ramping up for the surge in imminent logons to follow, we thought we’d revisit the issue to ramp up security awareness by sharing some of the more atrocious malware variants we’ve seen hitting the WoW gaming community.
Koobface: Not Just for Facebook, Anymore
![]() The latest generation of Koobface targets its particularly effective brand of social engineering at more social networks than ever. As the worm has evolved, we’ve seen it grow to encompass a pantheon of services, targeting more than just the widely publicized Facebook, MySpace, and Twitter, but a host of other Web sites where people meet and (apparently) post links of funny videos for one another to watch.
The latest generation of Koobface targets its particularly effective brand of social engineering at more social networks than ever. As the worm has evolved, we’ve seen it grow to encompass a pantheon of services, targeting more than just the widely publicized Facebook, MySpace, and Twitter, but a host of other Web sites where people meet and (apparently) post links of funny videos for one another to watch.
To illustrate how pervasive the worm has become at propagation, we put together the video below. (And no, you don’t need to download some random codec to watch it, just Flash.) If you’ve got two minutes, check it out, but to get the best view, maximize the video window first (click the little “X” next to “vimeo” in the lower-right corner):
[vimeo 6105480]
For our test, several members of Webroot’s Threat Research team created profiles on the social networks Koobface attempts to infiltrate, logged into those accounts on test computers, then executed the worm’s main installer application.
The worm checks to see which sites among the ones it targets that you’ve logged in to, and downloads specific payloads for each social networking site it targets. That makes sense: Each of those social networks has its own distinct user interface, which the payload targeting that site interacts with. But the sites all have one thing in common: They all permit members to send one another messages containing hotlinked URLs. And that’s what Koobface is best at: Propagating itself by sending links. Nothing surprised us more than finding that we could actually watch the worm interacting with the interface, filling in forms and clicking buttons, as we stared at the screen. read more…
Rogues Impersonate Google, Firefox Security Alerts
 In the past week, we’ve begun to see new fakealerts — those disturbingly effective, entirely bogus “virus warning” messages — that appear to impersonate the appearance and text of legitimate warning dialogs you might see while surfing with the Firefox browser, or searching Google. The dialog, in a stern, red dialog box on a gray background, reads “Warning! Visiting this site may harm your computer!” — a dialog that appears to be designed to evoke the look of a Google’s Safe Browsing advisory as displayed in Firefox.
In the past week, we’ve begun to see new fakealerts — those disturbingly effective, entirely bogus “virus warning” messages — that appear to impersonate the appearance and text of legitimate warning dialogs you might see while surfing with the Firefox browser, or searching Google. The dialog, in a stern, red dialog box on a gray background, reads “Warning! Visiting this site may harm your computer!” — a dialog that appears to be designed to evoke the look of a Google’s Safe Browsing advisory as displayed in Firefox.
Cast as a kind of split between a warning message and a clickwrap agreement, the text of the dialog box reads “This web site probably contains malicious software program, which can cause damage to your computer or perform actions without your permission. Your computer may be infected after visiting such web site. We recommend you to install (or activate) antivirus security software.”
At the bottom of the dialog box, two buttons, labeled “Continue Unprotected” and “Get security software” are preceded by the sentence “I do realize that visiting this site can cause harm to my computer.” I’d give them points for honesty, but I’d rather not give them points for anything.
Nothing happens when you click the “Continue Unprotected” button, and I’ll give you one guess what happens next when you click the “Get security software” button.
Steam Users Targeted by Phishers
 A phishing campaign that started around the beginning of the year, targeting gamers who use Valve Software’s Steam network, continues unabated but with a twist: The phishers have registered dozens of domain names, such as trial-steam.tk or steamcommunity###.tk (where the ### can be a two or three digit number), which are used to host the phishing pages. The pages appear to be a “Steam Community” login page which looks identical to Valve’s Steam Community Web site.
A phishing campaign that started around the beginning of the year, targeting gamers who use Valve Software’s Steam network, continues unabated but with a twist: The phishers have registered dozens of domain names, such as trial-steam.tk or steamcommunity###.tk (where the ### can be a two or three digit number), which are used to host the phishing pages. The pages appear to be a “Steam Community” login page which looks identical to Valve’s Steam Community Web site.
There are a few ways you can quickly identify whether you’re on the right page, or a fake. For one, the real Steam Community page is a secure HTTP page, so you should see the “https” in the address bar, and the lock icon in the corner of the browser window. By clicking on this icon, you can view the valid security certificate information, which clearly shows that the site is owned by Valve.
Another way you can tell that you’re on the correct Steam login page is to try using the “Select your preferred language” dropdown at the top of the window to change to any language other than English. If you’re on Steam’s page, the language will change; If you’re on the phisher’s page, it simply refreshes and remains set to English, no matter which language you pick. Also, the real Steam page features a cartoony graphic of “players” chatting amongst themselves which changes periodically. The phishers’ pages always have the same static graphic, shown above.
Read on for some additional details.
Trojans Replace Windows System Files
 When the threat research analysts here at Webroot recently started seeing malware swapping out legitimate components of Windows and replacing them with malware payloads, I couldn’t help but wonder what these malware authors were thinking.
When the threat research analysts here at Webroot recently started seeing malware swapping out legitimate components of Windows and replacing them with malware payloads, I couldn’t help but wonder what these malware authors were thinking.
After all, cybercriminals with a lick of sense know very well that messing with system files is dangerous juju. Such an act could, in the right (or should I say wrong) circumstances, render a PC inoperable, or at the very least, bogged down in crashes and instability. And for the authors of phishing malware, it would be incredibly thick-headed to do something to an infected system which might alert the user that something is wrong. After all, when it comes to stealing passwords, flying under the radar is the goal, otherwise the owner of the infected machine might hunt down the problem and remove the Trojan before it has a chance to do its work.
Well, it’s probably a good idea never to underestimate the stupidity of some malware authors. In the past four months, we’ve created new definitions for two phishing Trojans — Trojan-PWS-Mockworthy and Trojan-Phisher-Cassicant — that routinely replace system files with their own malicious payload. Removal is incredibly easy, but generates error messages on the system. That’s just annoying. The best news is, you don’t even need an antivirus product to restore a system file that’s been replaced in this way: A system sweep will remove the malicious components, and a service called Windows File Protection will find the correct system file on your Windows CD and replace it for you. Read on for some step-by-step instructions on just how to do that.
More Malware Trades on Tawdry Searches
 By now, you’ve most likely heard about how an ESPN reporter was victimized, and that a surreptitiously recorded video was distributed online. You may also have read that malware distributors were taking advantage of the high level of interest in this video to rapidly disseminate malware by convincing people to click links to malicious Web sites, including a fake CNN lookalike site, to watch said tawdry video.
By now, you’ve most likely heard about how an ESPN reporter was victimized, and that a surreptitiously recorded video was distributed online. You may also have read that malware distributors were taking advantage of the high level of interest in this video to rapidly disseminate malware by convincing people to click links to malicious Web sites, including a fake CNN lookalike site, to watch said tawdry video.
Well, that first wave of malware was almost identical to the distribution we saw when Farrah Fawcett died a few weeks ago. Web surfers were urged to click a link to download a picture of the late actress, and instead received an executable file which dropped, then downloaded, additional malware. Graham Cluley, who works for Sophos, pretty much nailed the story on his blog.
In our own research, we found the same things going on that he did: The piece of malware he describes (which we call Trojan-Downloader-Dermo) primarily engages in massive clickfraud, in which affiliates of advertising networks are paid each time someone clicks an advertisement in their browser. The software, in this case, is directed to “click” through hundreds of ads per minute. Occasionally, those “ads” exploit vulnerabilities in the browser to foist more malware onto the victim’s machine.
 But the malware distribution didn’t stop there. Seizing on the opportunity, another bunch of creep distributors of rogue antivirus products also began spreading the pain, using terms like “peephole video” to rank themselves high in search results. What we found was a rogue that not only lies about alleged infections on the victim’s computer, and features supposed endorsements from legitimate, respected technology publications — the award logos of PC World (and its UK counterpart PC Advisor), PC Magazine, and C|Net’s Computer Shopper grace its website — but spreads via a PDF file which exploits a relatively recently-disclosed vulnerability in Adobe’s Acrobat Reader software.
But the malware distribution didn’t stop there. Seizing on the opportunity, another bunch of creep distributors of rogue antivirus products also began spreading the pain, using terms like “peephole video” to rank themselves high in search results. What we found was a rogue that not only lies about alleged infections on the victim’s computer, and features supposed endorsements from legitimate, respected technology publications — the award logos of PC World (and its UK counterpart PC Advisor), PC Magazine, and C|Net’s Computer Shopper grace its website — but spreads via a PDF file which exploits a relatively recently-disclosed vulnerability in Adobe’s Acrobat Reader software.
Oh, Hush Chicken Little – The Sky is Not Falling: Why Cloud Security is Still Safe
By Brian Czarny
This week it was impossible to escape the “big news” that Twitter got hacked. The French hacker, known as “Hacker Croll,” who made headlines back in May for a similar Twitter breach, was at it again. This time he managed to get his hands on at least 310 sensitive Twitter business documents by gaining access to an employee’s email account, subsequently using information found in that account to then access the employee’s Google Apps account to steal the confidential company documents. The hacker sent the documents to TechCrunch, who then chose to publish them along with an account of the breach.
This highly publicized breach got people talking, and ignited a wave of speculation about two things: first, about the security of passwords and how easy it is to guess the answer to someone’s security question based on publicly available information found on social media sites; and second, about the security of data stored “in the cloud” – in this case, Google Apps.

Oh no, the sky is falling!
Our data isn’t safe in the cloud!
On the second point, let’s not take this too far. This incident has little to do with the security of the cloud apps themselves. It is much more about the first point and the security practices that users of all Web sites and applications – whether they are banking sites, social media sites or cloud applications – should be employing in their day-to-day use.
The key learning end users should take from this incident is that password security is critical, both in terms of the passwords you choose as well as the amount of data you expose publicly through social media sites like Twitter and Facebook.
Twitter spells this out on its blog response and even Hacker Croll himself articulates that his intention is to teach people a lesson about the security holes in secret questions:
“What I would like to say is that even the biggest and the strongest do silly things without realizing it and I hope that my action will help them to realize that nobody is safe on the net. If I did this it’s to educate those people who feel more secure than simple Internet novices. And security starts with simple things like secret questions because many people don’t realise the impact of these question on their life if somebody is able to crack them.”
What Keeps IT Professionals Up at Night
Webroot recently surveyed more than 300 email and Web security professionals about email management, compliance, archiving, encryption, spam, viruses, Web filtering and Web-based malware attacks. Our research shows that security practices and risk perceptions have evolved over the last year – the top three security concerns are email threat protection, data security/confidentiality and Web threat protection. Other highlights of the survey include:
- Security professionals are clearly worried about insufficient resources for Web security– a potential result of the economic downturn.
- The large number of organizations that were required to retrieve email for legal or compliance reasons within the last year indicates that email archiving services are becoming increasingly important.
- Most companies experienced some type of negative impact due to Web-based threats over the last 12 months, ranging from server outages and disrupted business activities to compromised data or transactions.
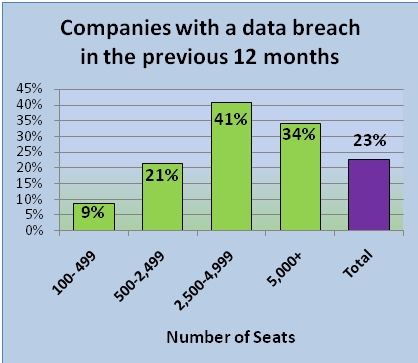
- 23% of survey respondents experienced a data breach – which cost between $10,000 and $1 million:
Just two weeks ago, Heartland Payment Systems disclosed that intruders hacked into the computers it uses to process 100 million payment card transactions per month for 175,000 merchants in one of the largest breaches on record. This past April, the Virginia Department of Health Professions learned that its Prescription Monitoring Program (PMP) computer system had been accessed by an unauthorized user – who then demanded $10 million to return over 8 million patient records and 35 million prescriptions.
As previously reported on this blog, Web threats are growing at a rapid pace in both volume and sophistication – fueled by the financial motivation of cybercriminals. Our research also showed that email threats were the top concern of IT professionals – but while email protection is important, the new vector of attack is the Web – and only 15% of organizations reported having Web security measures in place while 85% of new malware originates via the Web.
AutoCAD Adware Trojans Target Techies
 Every once in a while, you hear whispers or rumors about specially-crafted, targeted malware designed to steal a specific piece of data from a particular victim. The data thieves, in these limited cases, tend to be clever, thoughtful, and methodical in both the creation and deployment of their creations.
Every once in a while, you hear whispers or rumors about specially-crafted, targeted malware designed to steal a specific piece of data from a particular victim. The data thieves, in these limited cases, tend to be clever, thoughtful, and methodical in both the creation and deployment of their creations.
Rarely do malware researchers encounter these files. But it does happen occasionally, and I thought I had stumbled upon one of these kinds of spies a few weeks ago. It’s a peculiar Trojan horse which has been written not as a standard Windows application, but as an ObjectARX application — an application which can only run if you have AutoCAD, the engineering and design program from AutoDesk, installed on your PC.
Now, why do you suppose a malware author would write a Trojan that can only run on computers with AutoCAD; a Trojan that is so well designed that it prevents antivirus applications from running, and downloads specific, tailored updates for itself, depending on which version of AutoCAD the victim has on his or her PC?
Sounds a lot like a slick tool for corporate espionage, right? Well, not quite. Fark: It’s just another stupid adware client. We’re calling this dumb gimmick Trojan-Pigrig.























































