Cybercriminals continue diversifying their portfolios of standardized fraudulent services, in an attempt to efficiently monetize their malicious ‘know-how’, further contributing to the growth of the cybercrime ecosystem. In a series of blog posts highlighting the emergence of the boutique cybercrime-friendly E-shops, we’ve been emphasizing on the over-supply of compromised/stolen accounting data, efficiently aggregated through the TTPs (tactics, techniques and procedures) described in our “Cybercrime Trends – 2013” observations.
We’ve recently spotted a newly launched all-in-one cybercrime-friendly E-shop, offering a diversified portfolio of managed/DIY services/products, exposing a malicious infrastructure worth keeping an eye on. Let’s take a peek inside the E-shop’s inventory and expose the fraudulent infrastructure behind it.
More details:
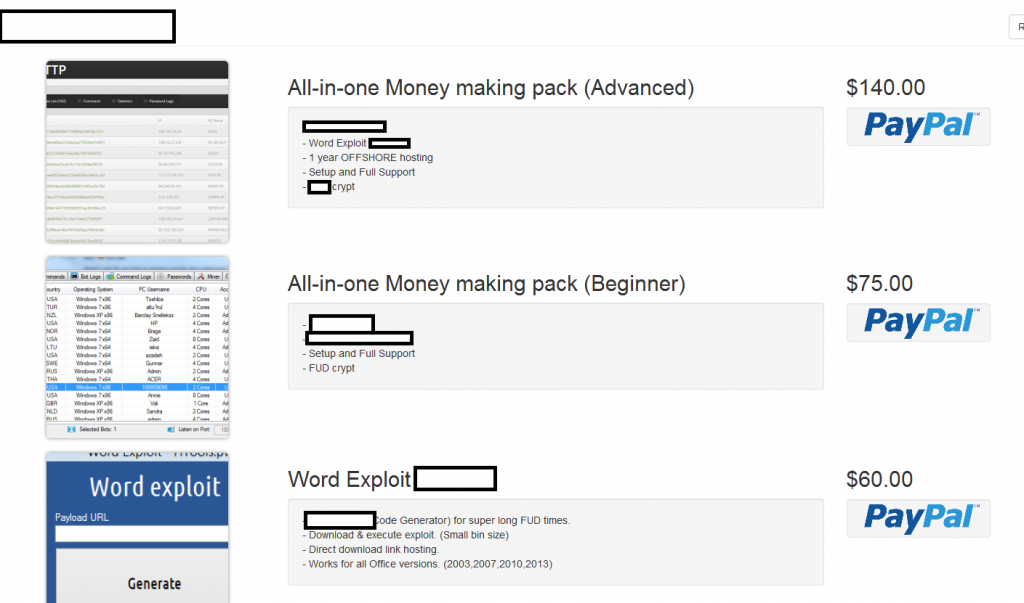
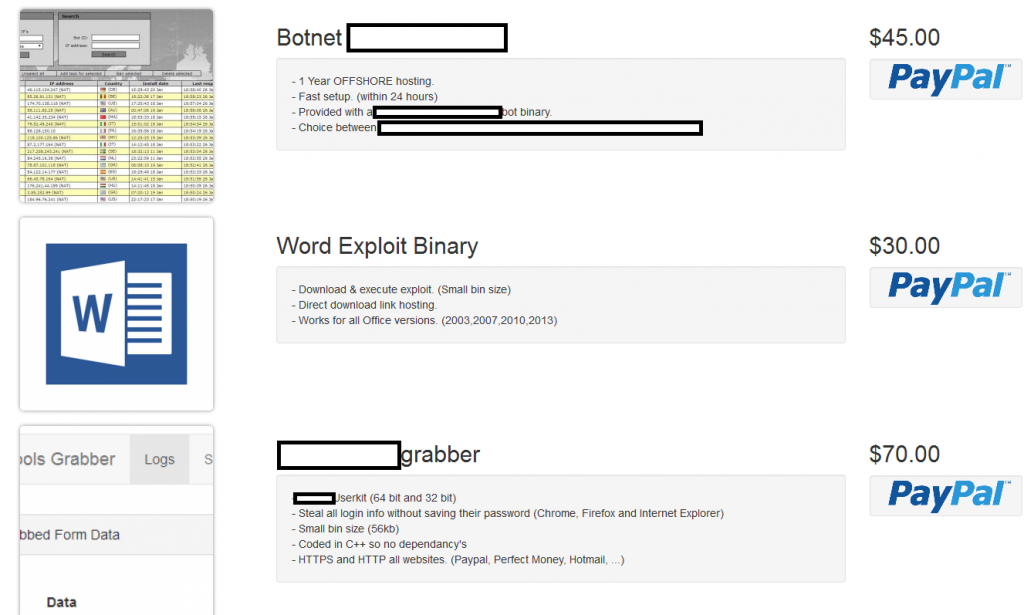
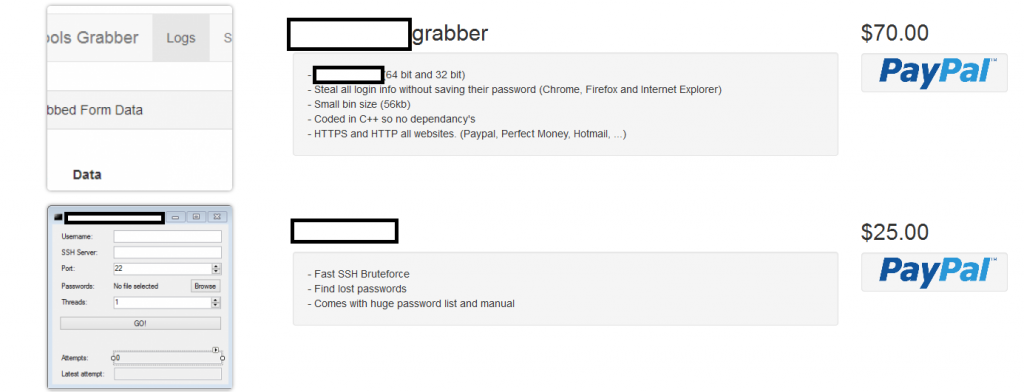
Sample screenshots of the all-in-one cybercrime-friendly E-shop:
The E-shop’s inventory currently consists of a DIY Word exploit generating tool, a malicious form grabbing tool, an SSH brute-forcing tool, as well as a managed cybercrime-friendly bulletproof hosting service. Let’s take a peek inside the actual malicious infrastructure.
Malicious MD5s known to have phoned back to the same C&C server (108.162.198.142) as the original hosting location:
MD5: 941a48eaad0fc20444005bb2a5ffa81f
MD5: b4c5b5e5c5e00dcf78bb5027af03766f
MD5: 42d83b9a5bbb142a7dc5bc27ee4f9933
MD5: 455645aad075326e93091861a3a370f3
MD5: 33d59790d4d3544afd6451254ec798b1
MD5: 5b62cc102f082cf442e49f09025b4188
Once executed MD5: 941a48eaad0fc20444005bb2a5ffa81f phones back to the following C&C servers:
162.159.242.119
193.36.43.104
198.41.184.67
141.101.113.135
185.11.125.93
173.194.41.120
162.159.247.204
144.76.86.115
162.159.249.242
173.194.41.115
Known to have phoned back to the same C&C server (162.159.242.119) are also the following malicious MD5s:
MD5: 941a48eaad0fc20444005bb2a5ffa81f
MD5: 43108272d3d5385bdee35017faef3e66
MD5: a0fdd6c0f47a3e11c7ff6ef733899285
MD5: 5ff93e6c88bd04c83350b9ce8190bcea
MD5: 0ebe5ca385d08d4e62206a7a04332d1d
MD5: 9926b031c7e7dcd2a35786aa78534be8
Malicious MD5s known to have phoned back to the same C&C server (108.162.199.142):
MD5: 24bb74c9625f3ae55ae17b68a3dc7d66
MD5: 43108272d3d5385bdee35017faef3e66
MD5: a0fdd6c0f47a3e11c7ff6ef733899285
MD5: 5ff93e6c88bd04c83350b9ce8190bcea
MD5: 49da13654fe67013ad67d4ba07327347
MD5: b1e7b397e266b826233567b881ae7e88
Webroot SecureAnywhere users are proactively protected from these threats.